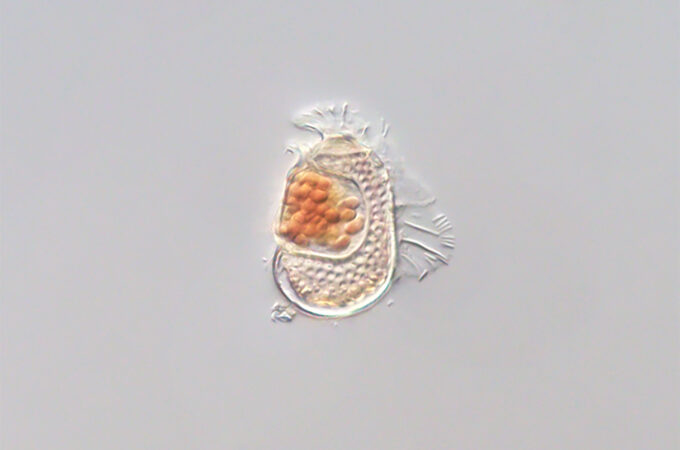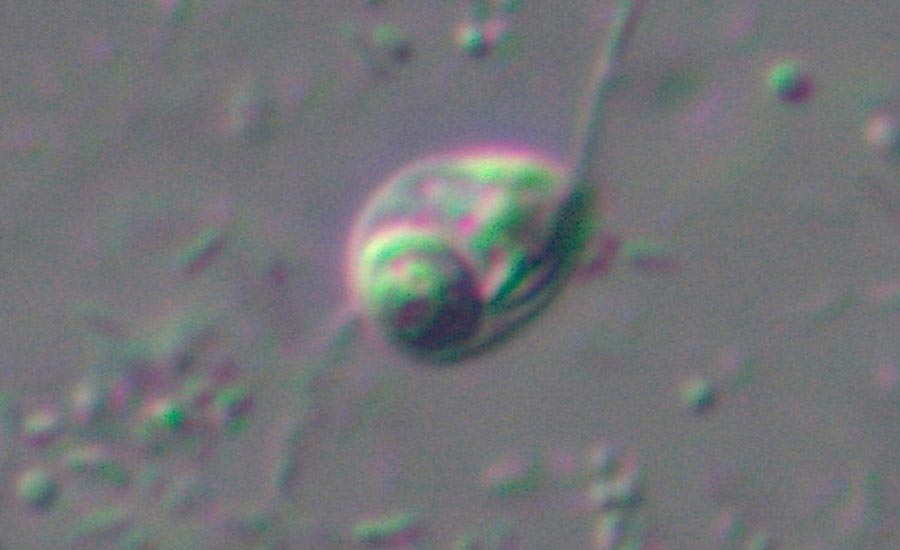
Ancoracysta twista is a predatory flagellate that uses its whip-like flagella to propel itself and unusual harpoon-like organelles, called ancoracysts, to immobilize other protists on which it feeds. This protist was discovered by Researchers at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego on a brain coral in a tropical aquarium. Thus its geographic origin in the wild is not known.
A. twista does not fit with any known group of organisms. Instead, it appears to belong to an early lineage of eukaryote that was previously unknown. The unusually large number of genes in its mitochondrial genome opens a window into the early evolution of eukaryotic organisms.